Docker Compose
Docker Compose is a tool provided by Docker that allows you to define and manage multi-container Docker applications. It simplifies the process of running and orchestrating multiple Docker containers as a cohesive application.
With Docker Compose, you can define the services, networks, volumes, and other configurations for your application in a single YAML file called a "docker-compose.yml" file. This file serves as a blueprint for your application's architecture and allows you to specify the relationships and dependencies between the containers.
YAML in Docker
YAML (YAML Ain't Markup Language) refers to a popular data serialization format that is human-readable and commonly used for configuration files, data exchange, and storing structured data.
In Docker, YAML (YAML Ain't Markup Language) is a human-readable data serialization format used for configuring and defining Docker Compose files. Docker Compose is a tool that allows you to define and manage multi-container Docker applications.
Task 1: Running Multiple Containers using Docker Compose
Get the repository
mkdir proj2 cd proj2 git clone https://github.com/Abhisek773/node-todo-cicd.git cd node-todo-cicdInstall docker-compose
sudo apt-get install docker-compose -y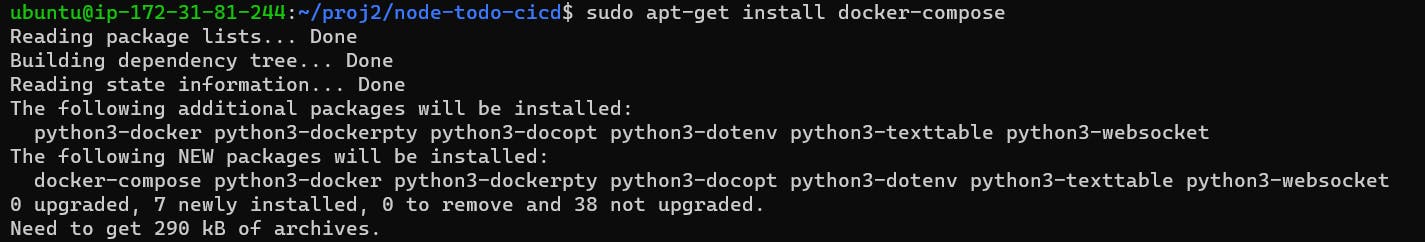
Create docker-compose.yaml file and configure all the details
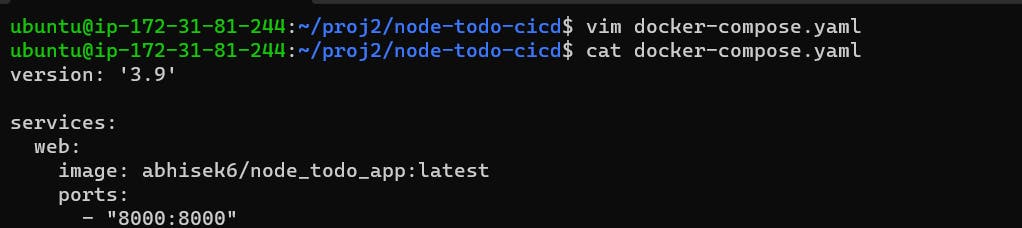
vim docker-compose.yaml #file contains version: '3.9' services: web: image: abhisek6/node_todo_app:latest ports: - "8000:8000"To start the container we use docker-compose up
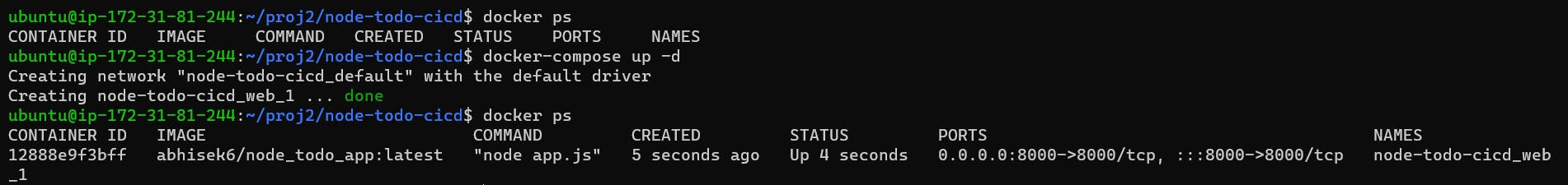
docker-compose up -dNow the application is up & running.
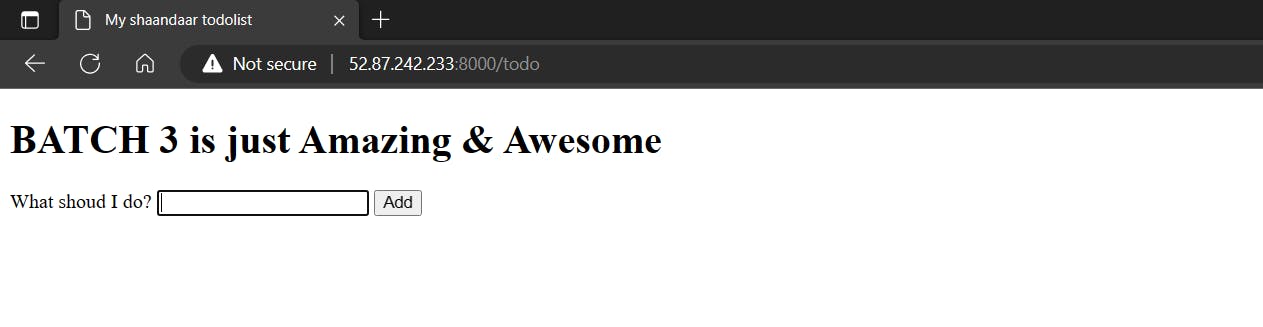
To bring down the application we use docker-compose.
docker-compose down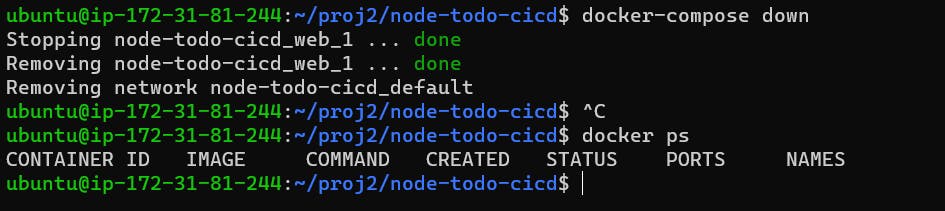
Task 2: Docker Commands
Pull a pre-existing Docker image from a public repository (e.g. Docker Hub) and run it on your local machine. Run the container as a non-root user (Hint- Use usermod command to give the user permission to docker). Make sure you reboot the instance after permitting the user.
docker pull abhisek6/react_django_app:latest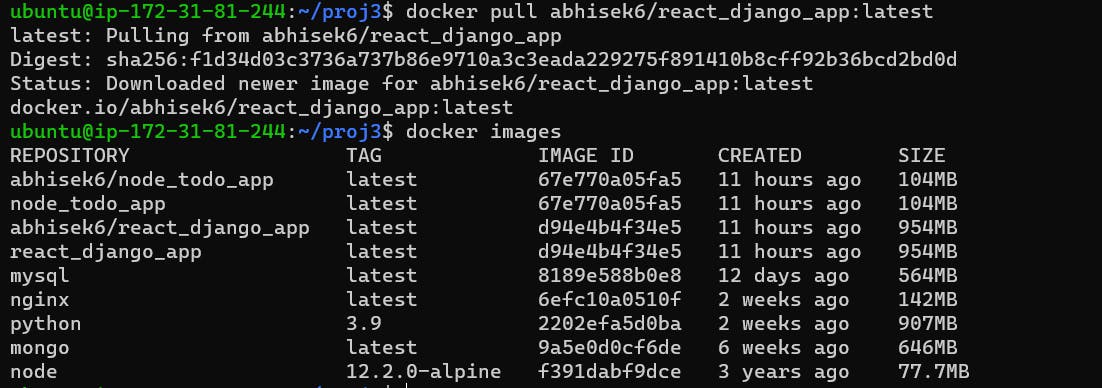
Inspect the container's running processes and exposed ports using the docker inspect command.
docker inspect <container_id>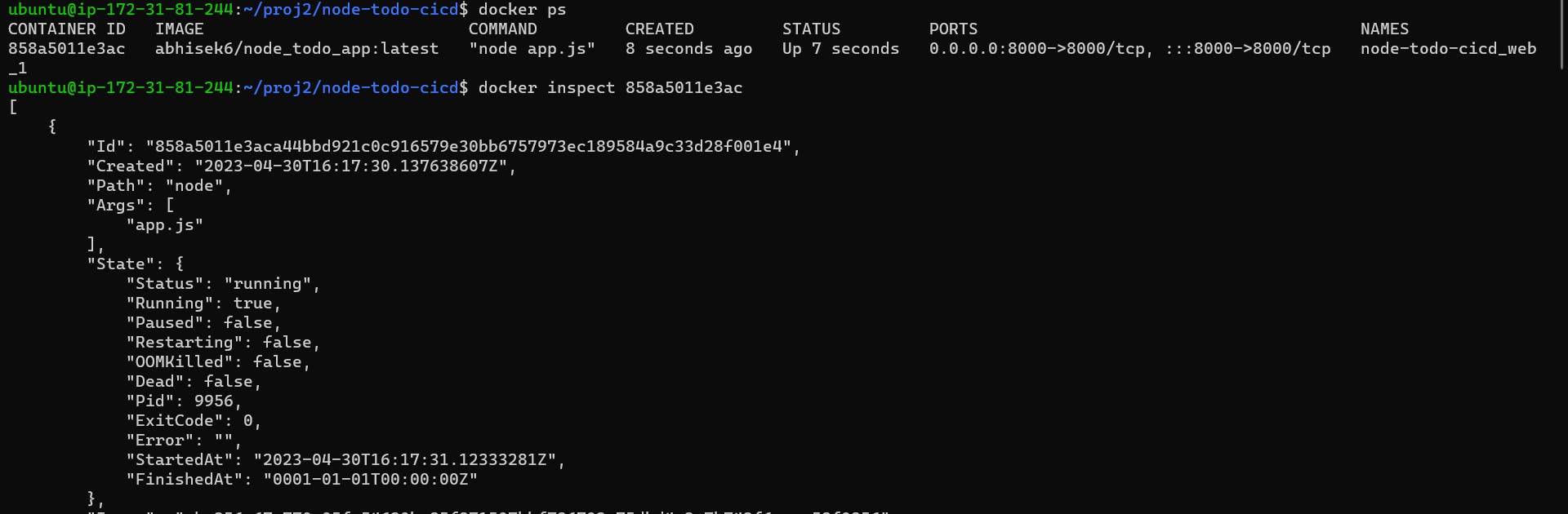
Use the docker logs command to view the container's log output.
docker log <container_id>
Use the docker stop and docker start commands to stop and start the container.
docker stop <container_id> docker start <container_id>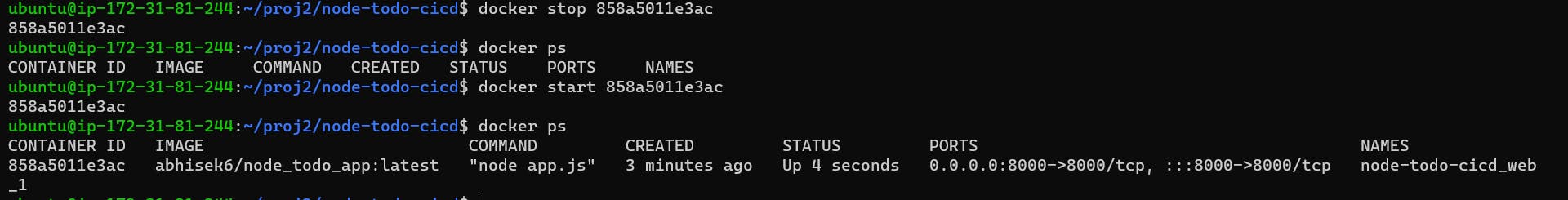
Use the docker rm command to remove the container when you're done.
# Before removing container it should be stopped first docker rm <container_id>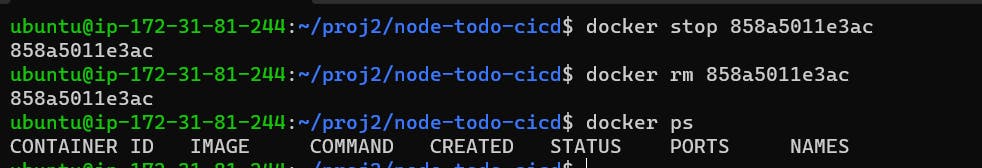
Thank You,
I want to express my deepest gratitude to each and every one of you who has taken the time to read, engage, and support my journey as a becoming DevOps Engineer.
Feel free to reach out to me if any corrections or add-ons are required on blogs. Your feedback is always welcome & appreciated.
~ Abhisek Moharana 😊